Related Products
Related Services
Related Reviews
nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR Array (H/M)
Benefits
• Focus–The prevalent Human tRFs&tiRNAs/Mouse tRFs having the highest biological potentials are profiled;
• Rigorous–All primer pairs are meticulously designed, optimized and validated;
• Convenient–Easy-to-use, ready-to-run, standard qPCR plate format for direct sample application. No sample pre-amplification is needed.
Applied with rtStar™ tRF&tiRNA Pretreatment Kit (CAT# AS-FS-005) to remove modifications in tRF & tiRNA before tRF&tiRNA cDNA library construction of qPCR, the PCR Arrays offer a new level of accuracy on the tRF&tiRNA detection.
In order to distinguish tRF&tiRNA from its precursor and achieve high specificity, rtStar™ First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (3’and 5’adaptor) (CAT # AS-FS-003 ) is required to be used with nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR Array for tRF&tiRNA detection.
Promo: 30% OFF! Valid through 3/31/2026
| Product Name | Catalog No. | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nrStar™ Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array | AS-NR-002-1 | 384-well (2*192) / plate | ||
| nrStar™ Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array (Roche Light Cycler 480) | AS-NR-002-1-R | 384-well (2*192) / plate | ||
| nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR | AS-NR-002M-1 | 384-well (4*96) / plate | ||
| nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR Array (Roche Light Cycler 480) | AS-NR-002M-1-R | 384-well (4*96) / plate |
tRFs & tiRNAs perform many biological functions to act as microRNAs in RNA interference; regulate target mRNA stability; assemble stress granules in response to cellular stress; modulate apoptosis; and pass on as epigenetic factors in intergenerational inheritance [1] (Fig. 1). The composition and abundance of tRFs&tiRNAs are highly dependent on the cell types and are associated with many disease conditions. The highly enriched presence in biofluids, often much more so than microRNAs, makes them excellent biomolecules for biomarkers [2-5].
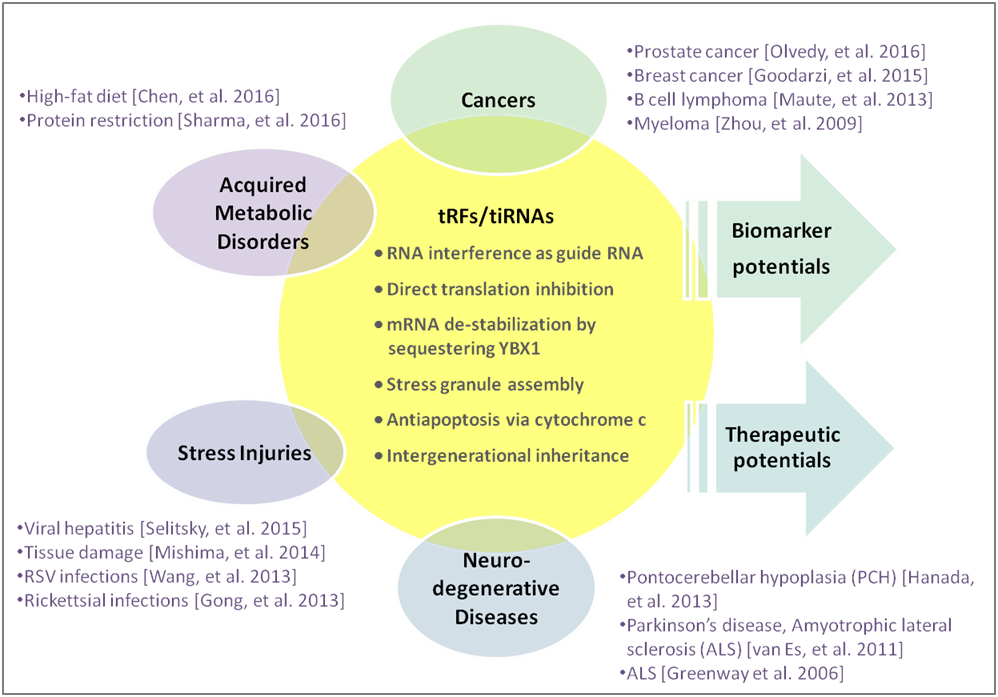
Figure 1. tRF & tiRNA functions and associated diseases.
tRF&tiRNAs are generated from tRNA or pre-tRNA through precise biogenesis processes. It is difficult to distinguish tRF&tiRNA from its precursor (tRNA or pre-tRNA) by conventional qPCR for their sharing of the same sequence. Moreover, length of tRFs&tiRNAs are 16~50 nt, too short to perform qPCR process. Arraystar exploit a smart system by introducing two artificial sequence to the 3’and 5’end of tRF&tiRNA, a famous and validated technology used in small RNA library preparation for sequencing. Corresponding forward and reverse primers targeting 5’and 3’ junction effectively discriminate tRF&tiRNA from its precursors and other small RNA, thus getting a reliable and accurate detection of tRF&tiRNA expression (Figure 2).
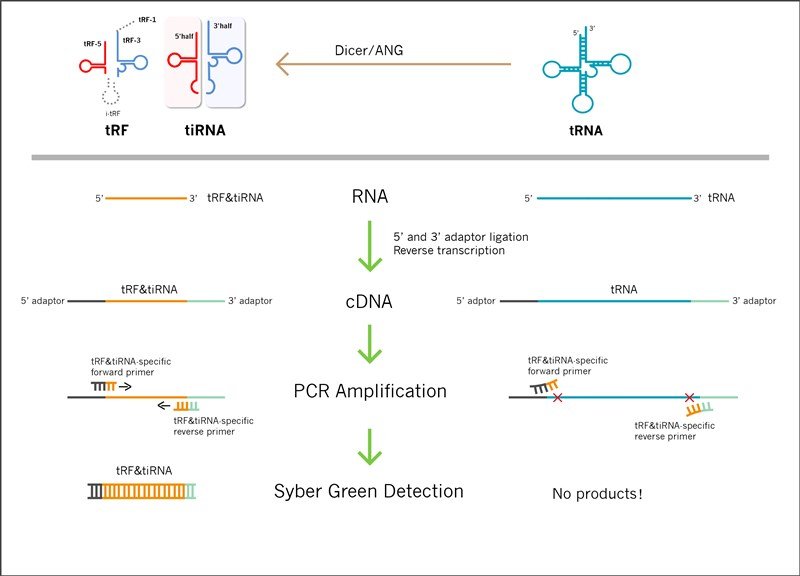
Figure 2. By introducing 5’and 3’adaptors, nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR panel detects the specific tRF&tiRNAs with no amplification of tRNAs or pre-tRNAs.
nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR Array System is designed to conveniently and quickly profile the tRFs & tiRNAs with high specificity, composed of two products: rtStar™ First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (3’and 5’adaptor) for adaptor ligation and cDNA synthesis, nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR Array for tRF&tiRNA detection.
Reference
1. Anderson P. and P. Ivanov (2014) “tRNA fragments in human health and disease.” FEBS Lett. 588(23):4297-304 [PMID: 25220675]
2. Telonis, A. G. et al. Dissecting tRNA-derived fragment complexities using personalized transcriptomes reveals novel fragment classes and unexpected dependencies. Oncotarget 6, 24797-24822, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.4695 (2015). [PMID: 26325506].
3. Olvedy, M. et al. A comprehensive repertoire of tRNA-derived fragments in prostate cancer. Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8293 (2016). [PMID: 27015120].
4. Schageman, J. et al. The complete exosome workflow solution: from isolation to characterization of RNA cargo. BioMed research international 2013, 253957, doi:10.1155/2013/253957 (2013). [PMID: 24205503].
5. Dhahbi, J. M. et al. 5′ tRNA halves are present as abundant complexes in serum, concentrated in blood cells, and modulated by aging and calorie restriction. BMC genomics 14, 298, doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-298 (2013). [PMID: 23638709].
6. Kumar, P., Mudunuri, S. B., Anaya, J. & Dutta, A. tRFdb: a database for transfer RNA fragments. Nucleic acids research 43, D141-145, doi:10.1093/nar/gku1138 (2015). [PMID: 25392422].
| Human tRFs&tiRNAs (185) |
|
tRF-1
1001, 1003, 1004, 1005, 1006, 1007, 1010, 1012, 1013, 1015, 1020, 1025, 1026, 1027, 1028, 1029, 1030, 1031, 1032, 1033, 1035, 1036, 1037, 1038, 1039, 1040, 1041, 1042
tRF-3
3002B, 3004B, 3006B, 3031B, 3033A, 3030A, 3030B, 3002A, 3003A, 3003B, 3006A, 3008A, 3008B, 3009B, 3011/12A, 3016/18/22B, 3017A, 3017B, 3019/20/21B, 3026B, 3027/28B, 3019A, 3020/21A, 3022A, 3026/27/28A, 3029A, 3031A
tRF-5
5001A, 5001B, 5002A, 5002B, 5008B, 5009A, 5009B, 5010A, 5011A, 5012B, 5013B, 5015/17A, 5016A, 5019A, 5019B, 5020/21A, 5020B, 5021B, 5022A, 5022B, 5023B, 5024A, 5026A, 5026/27B, 5028/29A, 5028/29B, 5032A, 5032B, TRF21-26, TRF63, TRF23, TRF205, TRF208, TRF223, TRF250, TRF272/274, TRF273, TRF293/294, TRF305/306/307, TRF308, TRF312, TRF316, TRF318, TRF320, TRF321, TRF322, TRF323/324/326, TRF337-339, TRF347, TRF351, TRF354, TRF356/359, TRF368, TRF366, TRF365, TRF373, TRF374, TRF375, TRF393, TRF396, TRF417, TRF457, TRF460, TRF462, TRF463, TRF466/468/469/471/472/473, TRF490, TRF492, TRF493, TRF511, TRF524, TRF533/534, TRF537, TRF546/547, TRF550/551
tiRNA-3 (3’ tRNA half)
3’tiR_007_GluTTC (n), 3’tiR_012_ArgCCT (n), 3’tiR_026_GlnCTG (n), 3’tiR_028_HisGTG (mt), 3’tiR_037_ArgCCG (n), 3’tiR_056_ValTAC (mt), 3’tiR_060_MetCAT (n), 3’tiR_063_ArgCCT (n), 3’tiR_075_GluTTC (mt)/ GluTTC (mt-la), 3’tiR_078_ArgTCT (n), 3’tiR_080_ProTGG (mt), 3’tiR_082_ThrTGT (mt), 3’tiR_088_LysCTT (n)
tiRNA-5 (5’ tRNA half)
5003/4C, 5008C, 5009C, 5016C, 5026/27C, TRF62, TRF315, TRF327, TRF353, TRF419, tiRNA-5033-ProTGG-1, tiRNA-5033-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5029-GlyGCC-2, tiRNA-5034-ValCAC-2, tiRNA-5034-ValCAC-3, tiRNA-5030-HisGTG-1, tiRNA-5030-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5033-GluTTC-2, tiRNA-5030-LysCTT-2, tiRNA-5029-ProAGG, tiRNA-5031-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5031-HisGTG-1, tiRNA-5031-GluCTC-1, tiRNA-5034-GlyCCC-1, tiRNA-5034-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5033-LysTTT-1, tiRNA-5032-LysTTT-1, tiRNA-5031-PheGAA, tiRNA-5034-ValTAC-3, tiRNA-5030-GlnTTG-3, tiRNA-5029-GlyGCC-3, tiRNA-5035-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5035-GluTTC-2, tiRNA-5034-GluTTC-2, tiRNA-5035-GluTTC-3, tiRNA-5032-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5035-GluCTC, tiRNA-5030-SerGCT-3, tiRNA-5030-SerGCT-1, tiRNA-5031-HisGTG-2, tiRNA-5029-AlaAGC-1, tiRNA-5032-LysCTT-1
|
| Mouse tRF (88) |
| tRF-1 1003, 1006, 1008, 1009, 1010, 1015, 1016, 1019, 1020, 1026, 1035tRF-3 3001b, 3002a/3035a, 3003a, 3004b, 3005a, 3006a, 3009a, 3009b, 3010a, 3010b/3017b, 3011a, 3011b, 3012b, 3017a, 3017b/3010b, 3019a, 3019b/3020b, 3021a, 3023b, 3024b/3046b, 3025a, 3025b, 3026a, 3027a, 3028b/3029b, 3029a, 3030a, 3031a, 3031b, 3032a, 3032b, 3033a, 3033b, 3034a, 3036a, 3036b/3037b, 3038a, 3038b, 3039a, 3041b/3042b, 3043a, 3043b, 3044a, 3044b, 3045a, 3046a, 3047b, 3048a, 3050a, 3051a, 3052atRF-5 5001a/5001b/5010a, 5002b/5004b, 5005a/5006b, 5005b, 5006a, 5006c, 5007a, 5009a, 5009b, 5011a, 5011b/5012b, 5012b, 5013a, 5013b, 5013b/5017b/5018b, 5014a, 5014a/5015a, 5014b, 5016a, 5019a, 5019b, 5020b/5021a, 5022a, 5022b, 5023b/24b |
Database
tRFdb http://genome.bioch.virginia.edu/trfdb/
MINTbase https://cm.jefferson.edu/MINTbase/
Reference
Olvedy, M. et al. A comprehensive repertoire of tRNA-derived fragments in prostate cancer. Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8293 (2016).
Selitsky SR, Baran-Gale J, Honda M, Yamane D, Masaki T, Fannin EE, et al. Small tRNA-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than microRNAs in chronic hepatitis B and C. Scientific reports 2015;5:7675.
Wang Q, Lee I, Ren J, Ajay SS, Lee YS, Bao X. Identification and functional characterization of tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs) in respiratory syncytial virus infection. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2013;21:368-79.

Figure 1. tRF&tiRNA qPCR array workflow.
Compatible qPCR Instruments Equipped with a 384-well Format Block:
• ABI ViiA™ 7
• ABI 7500 & ABI 7500 FAST
• ABI 7900HT
• ABI QuantStudio™ 5 Real-Time PCR system
• ABI QuantStudio™ 6 Flex Real-Time PCR system
• ABI QuantStudio™ 7 Flex Real-Time PCR system
• ABI QuantStudio™ 12K Flex Real-Time PCR System
• Bio-Rad CFX384
• Bio-Rad iCycler & iQ Real-Time PCR Systems
• Eppendorf Realplex
• Roche Light Cycler 480
Manual
 nrStar™ Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array_v1.05
nrStar™ Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array_v1.05
 nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR Array_v1.02
nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR Array_v1.02
![]() rtStar First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit Manual (3′ and 5′ adaptor)_v1.08
rtStar First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit Manual (3′ and 5′ adaptor)_v1.08
![]() rtStar™ First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit Manual (3′ and 5′ adaptor)(12 reactions)_v1.02
rtStar™ First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit Manual (3′ and 5′ adaptor)(12 reactions)_v1.02
Tool
![]() Analysis Tool for nrStar™ Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array_v2.01
Analysis Tool for nrStar™ Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array_v2.01
![]() Analysis tool for nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR Array_v2.01
Analysis tool for nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR Array_v2.01
Differentially expressed tRNA-derived fragments and their roles in primary cardiomyocytes stimulated by high glucose. Zhao Y, et al. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2023
Men who inject opioids exhibit altered tRNA-Gly-GCC isoforms in semen. Gornalusse G,et al. Molecular Human Reproduction, 2023
tRNA-derived fragment tRF-Glu49 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer by targeting FGL1. Wang Y, et al. Oncology Letters, 2022
Expression and Diagnostic Value of tRNA-Derived Fragments Secreted by Extracellular Vesicles in Hypopharyngeal Carcinoma. Xi J, et al. OncoTargets and therapy, 2021
Deletion of Endonuclease V suppresses chemically induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Kong X Y, et al. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020
A 3′-tRNA-derived fragment enhances cell proliferation, migration and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting FBXO47. Zhang F, et al. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2020
Maternal circulating syncytiotrophoblast-derived extracellular vesicles contain biologically active 5’-tRNA halves. Cooke W R, et al. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2019
